
Dr. Ruud W.M. Keunen
Innovator in TCD based Stroke Prevention and Perioperative Brain Monitoring
Dr. Ruud W.M. Keunen, former Dutch neurologist at the Haga HospitalThe Hague (1990–2020), is widely recognized for his pioneering work in stroke prevention, clinical neurophysiology, and neuro-intensive care. After his clinical career at Haga, he continued contributing to medical innovation and research and is now affiliated with the Eisenhower Clinic.
In 2021, Dr. Keunen received the Royal distinction Officer of the Order of Orange-Nassau for his exceptional contributions to patient safety and neurological care.
Advancing Embolus Detection Technology
Dr. Keunen has played a key international role in improving transcranial Doppler (TCD) diagnostics. He developed peer-reviewed algorithms capable of automatically detecting and distinguishing micro-embolic signals in the brain’s circulation. These tools:
- improve diagnostic accuracy
- support clinicians with objective embolus identification
- reduce the time spent on manual data review
The algorithms are now used worldwide, integrated into TCD systems produced by Delica in Shenzhen.
Through Keunen Medical, founded in 2008, he also created the educational platform www.embolusdetection.com, which provides clinicians and researchers with practical and scientific information on embolus detection.
The Haga Braincare Strategy
A major achievement during his years at Haga Hospital is the development of the Haga Braincare Strategy (HBS)—a comprehensive approach to preventing neurological complications during and after cardiac surgery.
The strategy combines:
- pre- and intra-operative TCD monitoring
- perioperative cerebral oximetry
- targeted interventions based on real-time findings
Studies in 2012 and 2017 showed that the HBS:
- significantly reduces postoperative delirium
- lowers the risk of hemodynamic stroke
- improves neurologic outcomes and patient safety
The HBS has since inspired similar brain-protective strategies both nationally and internationally.
Commitment to Team-Based Care
Throughout his career, Dr. Keunen has emphasized the importance of close collaboration between neurologists, anesthesiologists, cardiac surgeons, and neurophysiologists. His work continues to strengthen multidisciplinary care pathways aimed at protecting the brain during complex medical procedures.
Transcranial Doppler and Emboli Detection:
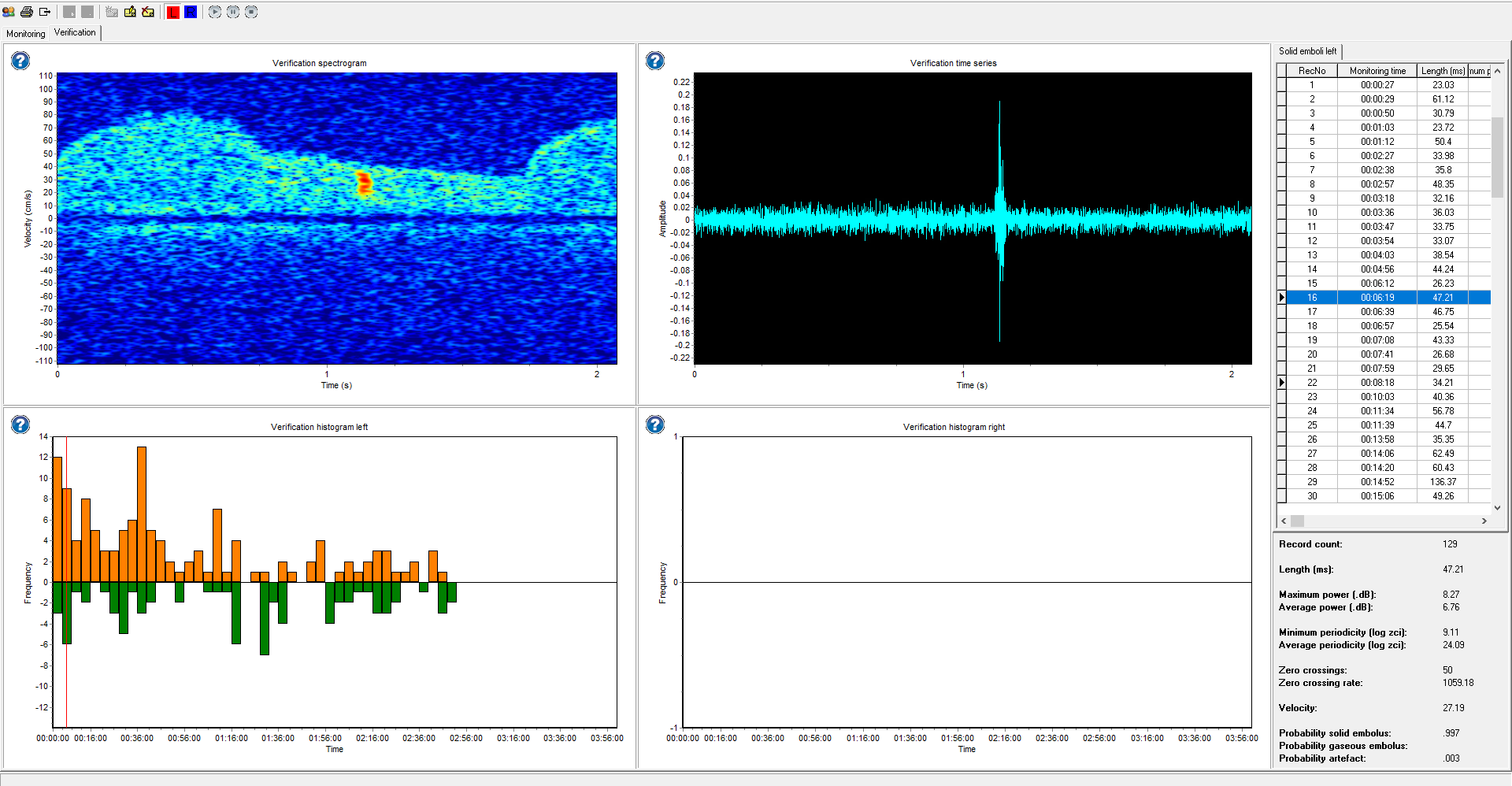
A micro-embolus is a tiny particle, often a blood clot, that travels through the bloodstream and becomes temporarily lodged within small vessels. When such a particle passes through the sample volume of a Transcranial Doppler (TCD) system, it produces a micro embolic signal (MES) — a short, high-intensity burst within the Doppler spectrum. Micro-emboli can originate from active embolic sources such as ulcerated carotid plaques or infected cardiac valves. These small emboli often precede larger “macro-emboli”, which may obstruct blood flow and cause Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs) or strokes. The presence of asymptomatic MES is considered one of the most important indicators of imminent stroke risk. Therefore, MES detection has become an essential tool in the prevention of TIAs and strokes. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD) is a highly sensitive, non-invasive, and safe method for detecting emboli in the cerebral circulation. During a typical examination, the middle cerebral arteries are monitored for approximately 30 minutes using 1.6/2 MHz transducers fixed securely with a headband. MES appear as short-lasting intensity increases in the Doppler velocity spectrum and produce characteristic “whistling,” “chirping,” or “clicking” sounds as they pass through the sample volume [1]. This unique sound pattern is caused by the regular zero-crossings of the embolic audio signal compared with the surrounding Doppler background [2].
For more details of the fundamentals of TCD embolus detection,
click the Lectures and Fundamental here to watch the video .
Click here Lecture and Fundamental to watch the video with Korean subtitle.
Clike here Lecture and Fundamental to watch the video with Spanish subtitle

Delica TCD and Emboli Detection
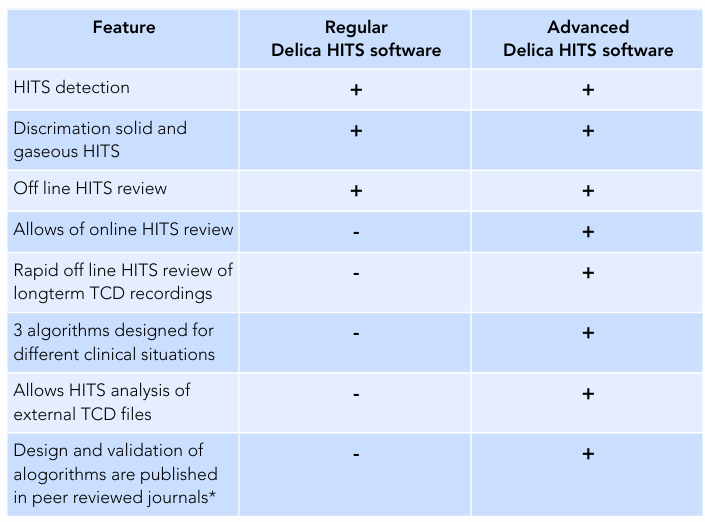
Accurate embolus recognition and analysis are among the key strengths of the Delica TCD systems. In addition to true MES, the TCD signal may also contain High-Intensity Transients (HITS) that arise from artifacts such as probe movements or speech. To address this, Delica offers two embolus detection software options: 1. 2. Regular Delica HITS software – the standard detection package included with all Delica TCD systems. Advanced Delica HITS software – a premium solution developed in collaboration with Dr. Keunen, a Dutch vascular neurologist and internationally recognized TCD expert. The Advanced Delica HITS software provides enhanced embolus detection accuracy and advanced analysis tools designed for clinical research and high-level diagnostic applications. The table below summarizes the main differences between the Regular and Advanced HITS software options. Depending on your clinical focus or research requirements, you can choose the standard configuration or upgrade to the Advanced Delica HITS detection system.
For more information, watch the Advanced HITS video by clicking the link here Delica advanced HITS detection to learn more.
* see References 2,3,4 References:
[1] Ringelstein EB, et al. Consensus on microembolus detection by TCD. International Consensus Group on Microembolus Detection. Stroke. 1998 Mar;29(3):725-9. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.3.725. PMID: 9506619.
[2] Keunen RW, et al. Introduction of an embolus detection system based on analysis of the transcranial Doppler audio-signal. J Med Eng Technol. 2008 Jul-Aug;32(4):296-304. doi: 10.1080/03091900701541265. PMID: 18666009.
[3] Keunen RW, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of an Algorithm for Discriminating Presumed Solid and Gaseous Microembolic Signals During Transcranial Doppler Examinations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023 Dec;49(12):2483-2488. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2023.08.011. Epub 2023 Sep
[4] Keunen RW, et al. Validation of an algorithm that separates gaseous micro-embolic signals and artifacts during transcranial Doppler persistent foramen ovale examinations, WFUMB Ultrasound Open, Volume 2, Issue 2,2024,100067,ISSN 2949-6683, https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.wfumbo.2024.100067 (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S2949668324000351).